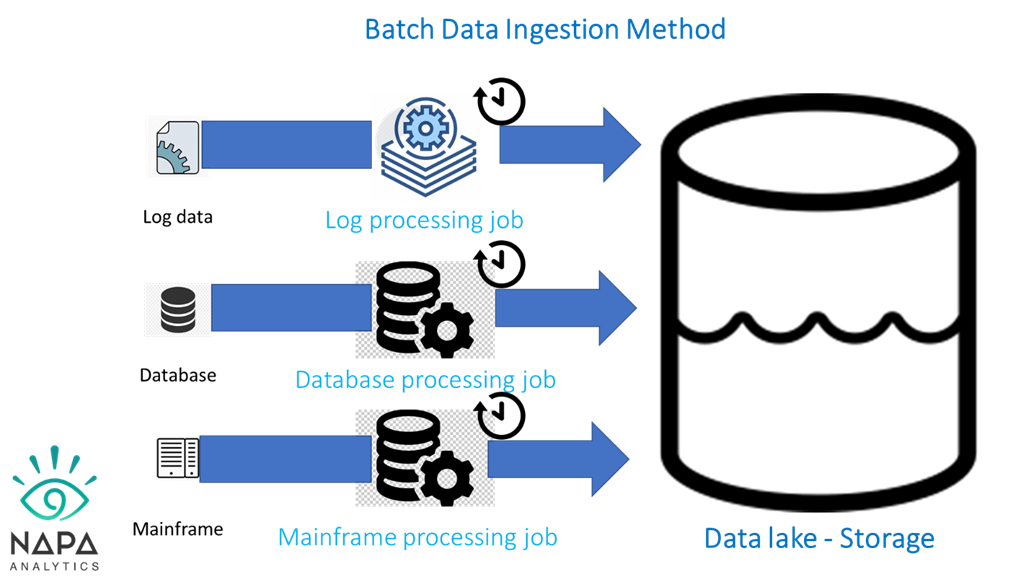
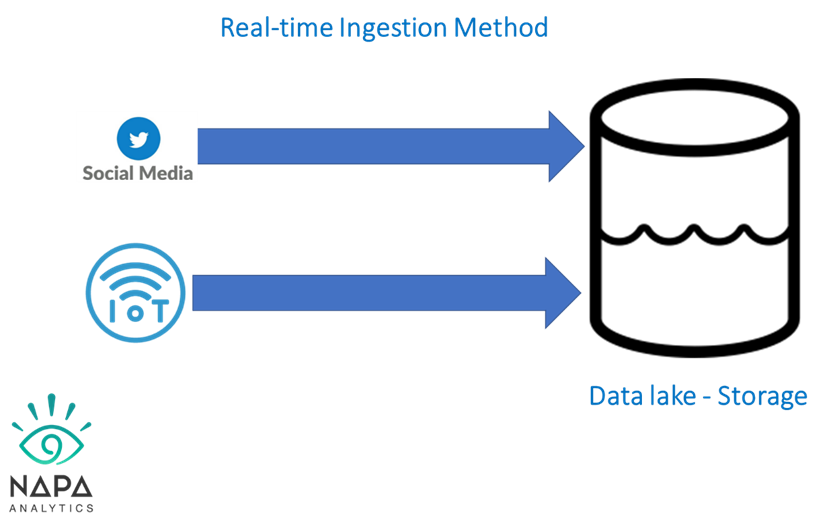
Mastering Data Quality: Implementing Effective Data Testing Strategies
In today’s data-driven world, ensuring high-quality data is crucial for making informed business decisions. To achieve this, implementing robust data testing strategies is essential. Let’s explore the fundamental aspects of data testing and how they contribute to maintaining data quality.
Core Concepts of Data Testing
Data testing is the systematic process of validating data to ensure its quality before it’s used for analysis or decision-making. It’s an essential practice in preserving data accuracy and reliability, focusing on error detection and prevention. High-quality data sets rely on proper testing to avoid cascading errors throughout data pipelines.
Data testing is vital for maintaining data observability, which allows businesses to monitor data flow and integrity in real-time. By doing so, it ensures that data pipelines remain dependable and functional. This visibility into data processes helps quickly identify anomalies and rectify them.
Accuracy, completeness, and consistency in data are crucial parts of quality testing. Accuracy ensures that data values are correct, completeness checks for missing information, and consistency verifies that data remains stable across systems. Together, these elements form the backbone of trustable data systems.
Data testing, therefore, plays a pivotal role in reinforcing these standards, enabling organizations to harness the power of their data efficiently.
Strategies for Effective Data Testing
In the realm of data testing, several strategies ensure data integrity. One such approach is using data diff, which helps to compare data sets, pinpoint discrepancies, and track changes over time. Automated testing is another pivotal strategy that brings forth efficiency by running a series of checks autonomously, minimizing human errors and saving time.
Employing tools like Datafold can elevate these testing processes. Datafold assists in detecting data anomalies early, offering a layer of verification for datasets. It supports developers by streamlining the task of identifying mismatches and discrepancies before escalating into larger issues.
Real-time monitoring becomes feasible with these strategies, enabling constant observation of data pipelines. Automated tests can run at scheduled intervals or when triggered by changes, ensuring that any issue is promptly flagged and addressed. This proactive approach helps maintain pipeline reliability and enhances data quality oversight.
Through the use of automated testing, businesses are able to simplify the complex process of data validation. By reducing human intervention in routine checks, the entire workflow becomes more seamless. This not only ensures that high data standards are met consistently but also allows data practitioners to focus their efforts on more strategic tasks. Integrating these methods can drastically improve both the pace and precision of data operations.
Conclusion
Implementing effective data testing strategies is crucial for maintaining high data quality. By integrating these practices into standard data management processes, organizations can ensure sustainable data health. Prioritizing data quality leads to better decision-making and enhances overall business performance.